Five Business Case Components Key for Using Extreme Networks 802.11ac Wave 2
All IT executives actually pursue the same goals: reducing costs, increasing end-user productivity, and matching IT operations to the organization’s business goals. It is clear that any technology that contributes to these goals should be carefully considered. These include those developed by Extreme Networks in the field of wireless networks.
- Extreme Networks develops and delivers managed network solutions that help IT organizations improve overall business results through closer relationships with customers, partners, and employees.
During the past five years, the value of the shares of Extreme Networks has not undergone significant changes, and in the last year, with the advent of Wave 2, steadily growing
- Today, Wi-Fi is the best technology and the most convenient connectivity for users, ─ in any organization and for almost all mobile devices and applications. Therefore, the high interest of customers in solutions based on the standard 802.11ac Wave 2, is not surprising.
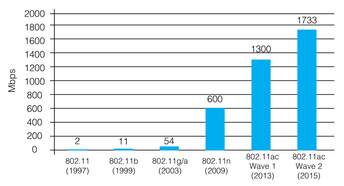
- Improvements in wireless technologies, radio design, access point construction, and implementation practices over the past two decades have already spawned several network generations: 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and now with 802.11ac ─ 1 Gb / s. In fact, 802.11ac Wave 2 achieves a throughput of 1,733 Gb / s.
- It is important that 802.11ac Wave 2 not only provides high throughput but also allows almost any device and transport connection to be used with more performance and less cost than ever before.
IT-managers today are forced to work with reduced budgets while demanding more and more efficiency. In this connection, the search for arguments to justify new investments from the point of view of business comes to the forefront.
The following are the five key components of the business case for using Wave 2.
1. Understanding the benefits of using Advanced Wireless Technologies
- When discussing wireless solutions, it’s customary to talk about their bandwidth. However, it is no longer the main problem of Wi-Fi, especially since we are talking about the generation of Wave 2 with 1.7 Gbps. This is quite enough to solve most modern corporate tasks.
- A much more important problem is to provide support for a large and growing number of users, devices and applications, many of which use real-time audio and streaming video.
- Even with a 33% improvement in peak bandwidth compared to Wave 1, Wave 2 technologies are evolutionary rather than revolutionary. They are based on the innovations of 802.11n and are not too different from the 802.11ac Wave 1.
- Improvements include greater spectral efficiency (fewer errors) and MIMO (Multiple Input / Multiple Output) – the ability to use space, not just frequency and time, which greatly improves throughput.
- An additional innovation, called “beamforming”, is also part of the 802.11ac standard. In a simplified way, beamforming is the ability to focus the broadcast in the direction that is optimal for the connections between the given access point and the client at any one time and to make real-time adjustments to compensate for movements and other conditions of the radio environment.
- To date, all but very few products on 802.11ac have provided at most three MIMO streams, each with a maximum throughput of 433.3 Mbps under optimal conditions. Wave 2 works with four streams, providing 1,733 Gb / s.
- Interestingly, the 802.11ac standard actually defines up to eight threads. However, products that do this in practice are unlikely to become common because of their complexity and cost (at least in the foreseeable future). In addition, today most devices on the client side support only one (rarely two) streams.
- Vawe 2 Multi-User MIMO technology allows multiple users to accept a transfer unique to each client with a single transfer from the given access point. That is, there is no need to wait for other users to be served and wasted potential bandwidth. As a result, efficiency is dramatically increased along with end-user productivity.
2. Maximum use of capital investments
- Capital Expenditures (CapEx) are limited in the IT budgets of almost all companies, starting with the recession in 2008. At the same time, the continuous flow of innovations in IT continues to affect both the infrastructure and the replacement cycles of equipment, albeit in somewhat more Slower pace than it was in the past. And, of course, careful consideration of absolute costs, and especially ROI, should now be part of all decisions about capital investments.
- As noted, for wireless LAN, the price/performance ratio improves with each new generation of products. But, in fact, this is due to an increase in their throughput, ─ while prices for certain equipment (access points, etc.) remain unchanged or slightly reduced.
- The 802.11ac Wave 2 products are fully backward compatible with Wave 1 (and even with 802.11n). They work better than their predecessors because they have better system architecture and firmware. Improvements have also affected their installation in a corporate environment, which typically becomes seamless and stable.
- Such an improvement in the price/performance ratio with minimal installation costs raises an important question ─ is it really time to replace existing Wi-Fi solutions with Wave 2. There is no unambiguous answer. Each organization must evaluate the purchase in terms of its depreciation cycles, available financial resources and a combination of the entire IT infrastructure and IT strategy of the enterprise.
- However, it is obvious that any 802.11g (or earlier) solutions are definitely ripe for replacement, as too much has changed to a date in terms of the technical capabilities and value of WLAN. Operating systems on 802.11n will experience ever-increasing pressure from Wave 2, especially if it makes sense to take advantage of the advantages of MU-MIMO.
3. Reducing operating costs
By definition, CapEx plus OpEx is the total cost of ownership (Total Cost of Ownership, TCO). This is a key metric in determining the return on investment (ROI) and estimating capital costs over time.
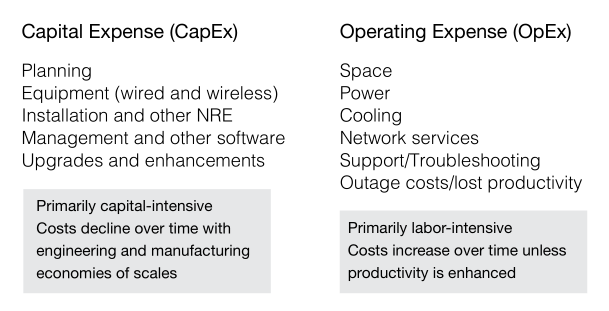
- While the component of the capital costs of 802.11ac Wave 2 is quite understandable, operating costs (Operating Expense, OpEx) are somewhat more complex subject for consideration. The reason for this is that OpEx consists of such aspects as monitoring, management, support, troubleshooting, etc. They require the attention of qualified IT specialists.
- Unlike CapEx, the OpEx indicator tends to increase over time ─ people become more expensive due to inflation and competition for special skills. With this problem, businesses often cope, increasing the productivity of IT staff.
- Therefore, the implementation of Wave 2 promises a significant increase in the productivity of IT department staff. First of all, improved WLAN performance (bandwidth, capacity, and support for time-limited communications, such as voice and video) will result in fewer calls to technical personnel. In addition, Wave 2 will give improved control and analytics, visibility of results and less time for troubleshooting.
- And, finally, regardless of how Wave 2 is implemented, ─ as a new deployment or as an upgrade, ─ flexible, stable and cheap seamless scalability is an integral part of Wave 2. Thus, any IT staff costs associated with deploying Wave 2, are also minimized.
4. Increase the productivity of end users
Any network strategy is best evaluated in terms of increasing the productivity of end users served by the network. As noted above, the number of users of wireless networks is constantly growing, ─ and not only in terms of the number of company personnel.
- The spread of the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) trend has caused a greater demand for services from users with several simultaneously active devices than ever before. Today, you can often meet users who are simultaneously connected to a wireless network by two devices (smartphone and tablet). It is not uncommon to use three or four devices at the same time.
- None of these devices (like the users themselves) like networks that are slow, unavailable in certain locations, unreliable or not meeting the increasing needs, including support for streaming media, real-time telephony and other “heavy” communications.
- New applications for Internet of Things (IoT) also put forward additional requirements for wireless networks. Of course, many IoT solutions will continue to operate relatively little traffic. However, there are also quite heavy services, such as, for example, video surveillance and real-time processes. This means that the Wi-Fi network in which they operate will have needs at the Wave 2 level.
- The more reliable and affordable the wireless LAN, the higher the performance of end users. Therefore, to distribute wireless services in virtually any organization, more MIMO and MU-MIMO streams are required.
- The bottom line of Wave 2 is that relatively small investments in new technologies can already today provide a significant reduction in operating costs by maximizing productivity, and thus reducing TCO and increasing ROI.
5. Related network technologies
Products based on 802.11ac Wave 2, embody the latest advances in features and technologies to optimize the entire chain of wireless networking. This applies to mobile clients, access points, controllers, switches and routers, control systems, and so on.
Wave 2 is the technological basis for modern wireless LANs. The network infrastructure will increasingly depend on the new and capabilities realized in products based on Wave 2. Here are the main ones.
- Switching. Wave 2 will require that the power technology via Ethernet PoE + realizes its full potential.
- Management. This function includes context-controlled monitoring, alerts and alerts, reporting, auditing, and more.
- Analytics. It is defined as a set of abilities designed to study large amounts of data in conditions of uncertainty, ie when it is difficult to accurately determine the subject of a search.
- Advanced Security. Security is always one of the key elements in any network. The function WPA2 Wi-Fi (which, of course, remains important) is used less and less. Increasingly, security depends on other means of the network, which are based on identification, access policies, context, content filtering, etc.
- The Cloud. The key trend of today in the deployment of both wired and wireless networks is management and related functions in the cloud. The main advantages of cloud-based management are easy turnkey implementation, simple scalability, fault tolerance and increased security. The benefit in the cost of such an approach is also significant, as CapEx’s capital investments thus become a very economical option for OpEx.
- SDN. Software-defined networks will play a much larger role in both wired and wireless networks in the years to come. Using SDN improves network security, solution integrity, simplifies implementation, provides more comprehensive and better management and analytics than traditional solutions.
Given the continuous flow of innovation in Wi-Fi technologies and systems, there is one more question – how soon will the next technology appear that will be able to displace Wave 2?
- Indeed, the IEEE 802 Standards Committee is working on new, even higher standards, but they are expected only in three years and will take at least five years before any of them become the main trend in practice. Thus, the payback period for Wave 2 will be quite long, with good economic justification.
Wave 2 Examples
This section discusses the benefits of using Wave 2 solutions in public places, education, industrial production, corporate office networks and healthcare.
- Wave 2 in public places. Wireless traffic is growing rapidly in the hotel industry, in sports, in entertainment venues. All of them are characterized by a high density of users and devices. This motivates the demand for Wave 2 802.11ac.
Both problems and solutions for wireless LANs are often determined precisely in terms of density. Requirements, in the end, only grow with time. An example is IOT with its many new consumer devices, services, and other applications.
- Wave 2 in education. The field of education has always been one of the main consumers of wireless LANs. In the end, who consumes more bandwidth than students, especially as the share of streaming video increases in the learning process? And who would want to study at a school where there would not be Wi-Fi?
But still, budget constraints often force many IT managers of educational institutions to use outdated systems. Wave 2 is a big step forward in solving this problem, providing greater bandwidth and being more cost-effective than any previous generation of Wi-Fi.
In addition, the redundant capabilities of Wave 2 mean that the lifetime of these networks will be long enough. In a rather conservative educational environment of the IT environment, this is an important factor.
- Wave 2 in production. The production environment, as a rule, is rather complicated for setting up Wi-Fi services. Reliability is the most important element for wireless solutions in shops and distribution centers, as they are associated with the management of continuous flows and business processes. There may be adverse climatic conditions and radio frequency interference. In this respect, Wave 2 is ideally suited to the production environment, ensuring the continuity and flexibility of production in any environment.
- Corporate Wave 2. Almost every enterprise today, like most government organizations, depends on Wi-Fi as the main communication. In such conditions, Wave 2 is the foundation upon which corporate wireless network solutions will be built for quite a long time.
- Wave 2 in Health Care. No IT environment is more demanding than in healthcare. Here the main requirement is reliability in medical information systems for solutions related to human life …
Therefore, much depends on the wireless LAN providing better protection, capabilities, and reliability for patient communications and telemetry, as well as short-latency access to large (and often very large) amounts of data produced by computed tomography (CT) devices and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Wave 2 is in this respect the best technology for the healthcare industry.
Assortment of Wave 2 Extreme Networks
- Today the company offers a variety of access points, including outdoor-protected outdoor devices, controllers for wireless networks, as well as control software.
ExtremeWireless Access Points
- The ExtremeWireless access points provide the performance of modern wired networks for the surrounding high-density network environment. Smart Access Points are equally well suited for both distributed and centralized deployment models.


Outdoor Access Points
- The access point family is designed for outdoor deployment in a non-permanent climate environment-for example, for open-air events, etc. They also provide seamless roaming in multiple campus subnets without the need for heavy client software.

Controllers (ExtremeWireless Controllers)
- ExtremeWireless controllers are easy to deploy and manage. They provide high functionality, allowing organizations to determine how wireless traffic, audio, and video data will be processed without architectural constraints and in accordance with the needs of the organization.


Extreme Management
ExtremeManagement
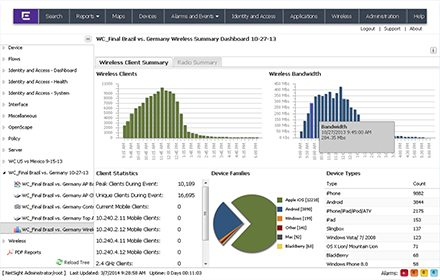
ExtremeManagement keeps everything under control, using role-based access controls and a single control panel. At the same time when managing the network using ExtremeManagement with one click, you can perform a number of actions.
Conclusion
- Of course, the business case for a new solution for each organization is unique, but it is clear that Wave 2 is already here and offers real benefits for any organization that uses IT. Features such as aggregate throughput of 1.7 Gb / s and multi-user MIMO are not available in any other generation of Wi-Fi products.
- The excellent price/performance ratio and the possibility of seamless integration into the corporate IT infrastructure remove all issues regarding capital costs. A sharp increase in productivity – for both IT staff and end users – reduces operational costs, minimizing TCO and maximizing ROI. Additional network capabilities in switching, management, analytics, security, and SDN work naturally with Wave 2, together providing a sufficient business case.
In other words, the time to implement and use 802.11ac Wave 2 has already come.





